
This harpsichord is the work of two celebrated makers: originally constructed by
Andreas Ruckers in Antwerp (1646), it was later remodeled and expanded by
Pascal Taskin in Paris (1780).
A
harpsichord is a
musical instrument played by means of a
keyboard. It produces sound by plucking a string when a key is pressed.
"Harpsichord" designates the whole family of similar plucked keyboard instruments, including the smaller
virginals,
muselar, and
spinet.
The harpsichord was widely used in
Renaissance and
Baroque music. During the late 18th century, it gradually disappeared from the musical scene with the rise of the
piano. But in the 20th century, it made a resurgence, being used in
historically informed performance of older music, in new (contemporary) compositions, and in popular culture.
Mechanism[edit]
Harpsichords vary in size and shape, but all have the same basic functional arrangement. The player depresses a key that rocks over a pivot in the middle of its length. The other end of the key lifts a
jack (a long strip of wood) that holds a small
plectrum (a wedge-shaped piece of
quill, nowadays often plastic), which plucks the string. When the player releases the key, the far end returns to its rest position, and the jack falls back. The plectrum, mounted on a tongue that can swivel backwards away from the string, passes the string without plucking it again. As the key reaches its rest position, a felt damper atop the jack stops the string's vibrations. These basic principles are explained in detail below.

Figure 1. Schematic view of a 2 × 8' single manual harpsichord
- The keylever is a simple pivot, which rocks on a balance pin that passes through a hole drilled through the keylever.
- The jack is a thin, rectangular piece of wood that sits upright on the end of the keylever. The jacks are held in place by the registers. These are two long strips of wood (the upper movable, the lower fixed), which run in the gap between pinblock and bellyrail. The registers have rectangular mortises (holes) through which the jacks pass as they can move up and down. The registers hold the jacks in the precise location needed to pluck the string.

Figure 2. Upper part of a jack
- In the jack, a plectrum juts out almost horizontally (normally the plectrum is angled upwards a tiny amount) and passes just under the string. Historically, plectra were made of bird quill or leather; many modern harpsichords have plastic (delrin or celcon) plectra.
- When the front of the key is pressed, the back of the key rises, the jack is lifted, and the plectrum plucks the string.
- The vertical motion of the jack is then stopped by the jackrail (also called the upper rail), which is covered with soft felt to muffle the impact.

Figure 3: how the harpsichord action works
- When the key is released, the jack falls back down under its own weight, and the plectrum passes back under the string. This is made possible by having the plectrum held in a tongue attached with a pivot and a spring to the body of the jack. The bottom surface of the plectrum is cut at a slant; thus when the descending plectrum touches the string from above, the angled lower surface provides enough force to push the tongue backward.[1]
- When the jack arrives in fully lowered position, the felt damper touches the string, causing the note to cease.
Strings, tuning, and soundboard[edit]

Sound board of a harpsichord with
Chladni patterns

Detail of the harpsichord by Karl Conrad Fleisher; Hamburg, 1720 in
Museu de la Música de Barcelona. A decorative rose descends below the soundboard in which is it mounted; the soundboard itself is adorned with floral painting around the rose. The bridge is at lower right.
Each string is wound around a tuning pin, normally at the end of the string closer to the player. When rotated with a wrench or tuning hammer, the tuning pin adjusts the tension so that the string sounds the correct pitch. Tuning pins are held tightly in holes drilled in thepinblock or wrestplank, an oblong hardwood plank.
Proceeding from the tuning pin, a string next passes over the nut, a sharp edge that is made of hardwood and is normally attached to the wrestplank. The section of the string beyond the nut forms its vibrating length, which is plucked and creates sound.
At the other end of its vibrating length, the string passes over the
bridge, another sharp edge made of hardwood. As with the nut, the horizontal position of the string along the bridge is determined by a vertical metal pin inserted into the bridge, against which the string rests.
The bridge itself rests on a
soundboard, a thin panel of wood usually made of
spruce,
fir or—in some Italian harpsichords—
cypress. The soundboard efficiently transduces the vibrations of the strings into vibrations in the air; without a soundboard, the strings would produce only a very feeble sound.
A string is attached at its far end by a loop to a hitchpin that secures it to the case.
Multiple choirs of strings[edit]
While many harpsichords have exactly one string per note, more elaborate harpsichords can have more. This provides two advantages: ability to vary volume and ability to vary tonal quality. Volume is increased when the mechanism of the instrument is set up by the player (see below) so that the press of a single key plucks more than one string. Tonal quality can be varied in two ways. First, different choirs of strings can be designed to have distinct tonal qualities, usually by having one set of strings plucked closer to the nut, which emphasizes the higher
harmonics, and produces a "nasal" sound quality; the mechanism of the instrument permits the player to select one choir or the other. Second, having one key pluck two strings at once changes not just volume but also tonal quality; for instance, when two strings tuned to the same pitch are plucked simultaneously, the note is not just louder but also richer and more complex. A particularly vivid effect is obtained when the strings plucked simultaneously are an
octave apart. This is normally heard by the ear not as two pitches but as one: the sound of the higher string is blended with that of the lower one, and the ear hears the lower pitch, enriched in tonal quality by the additional strength in the upper harmonics of the note sounded by the higher string.
When describing a harpsichord it is customary to specify its choirs of strings, often called its
disposition. Strings at
eight foot pitch sound at the normal expected pitch, strings at four foot pitch sound an octave higher. Harpsichords occasionally include a sixteen-foot choir (one octave lower than eight-foot) or a two-foot choir (two octaves higher; quite rare).
When there are multiple choirs of strings, the player is often able to control which choirs sound. This is usually done by having a set of jacks for each choir, and a mechanism for "turning off" each set, often by moving the upper register (through which the jacks slide) sideways a short distance, so that their plectra miss the strings. In simpler instruments this is done by manually moving the registers, but as the harpsichord evolved, builders invented levers, knee levers and pedal mechanisms to make it easier to change registration.
Harpsichords with more than one keyboard
[2] provide flexibility in selecting which strings play, since each manual can control the plucking of a different set of strings. In addition, such harpsichords often have a mechanism that couples manuals together, so that a single manual plays both sets of strings. The most flexible system is the French shove coupler, in which the lower manual slides forward and backward. In the backward position, "dogs" attached to the upper surface of the lower manual engage the lower surface of the upper manual's keys. Depending on choice of keyboard and coupler position, the player can select any of the sets of jacks labeled in figure 4 as A, or B and C, or all three.
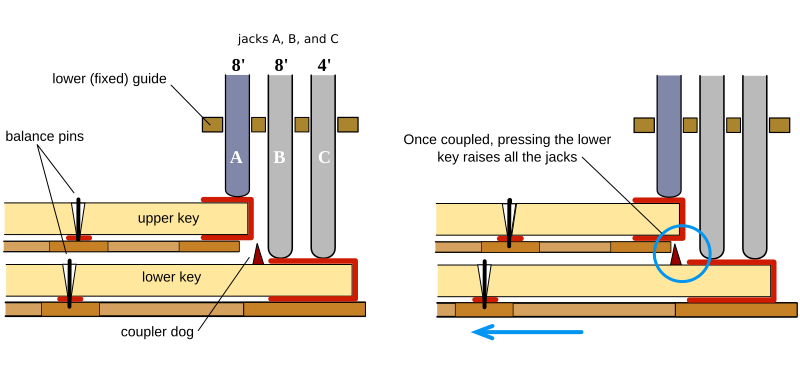
Figure 4. French shove coupler. To the left: uncoupled keyboards. The depressed upper key lifts the jack A upwards. The depressed lower key lifts jacks B and C. To the right: The upper keyboard is coupled to the lower one by pulling the latter. The depressed upper key lifts the jack A upwards. The depressed lower key lifts jacks A, B and C.
The English dogleg jack system (also used in Baroque Flanders) does not require a coupler. The jacks labeled A in Figure 5 have a "dogleg" shape that permits either keyboard to play A. If the player wishes to play the upper 8' from the upper manual only and not from the lower manual, a stop handle disengages the jacks labeled A and engages instead an alternative row of jacks called "lute stop" (not shown in the Figure).
[3]
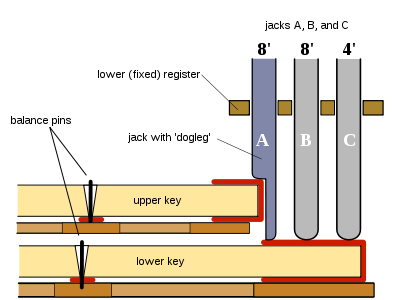
Figure 5. Dogleg jack, English coupler system. When depressed, the upper key lifts the "dogleg" jack (jack A) upwards. The lower key lifts all three jacks A, B, and C.
The use of multiple manuals in a harpsichord was not originally provided for the flexibility in choosing which strings would sound, but rather for
transposition. For discussion, see
History of the harpsichord.

Jan Vermeer's famous painting
A Lady Standing at a Virginal shows a characteristic practice of his time, with the instrument mounted on a table and the player standing.
The case holds in position all of the important structural members: pinblock, soundboard, hitchpins, keyboard, and the jack action. It usually includes a solid bottom, and also internal bracing to maintain its form without warping under the tension of the strings. Cases vary greatly in weight and sturdiness: Italian harpsichords are often of light construction; heavier construction is found in the later Flemish instruments and those derived from them (see
History of the harpsichord).

A false inner-outer harpsichord from the
Deutsches Museum in
Munich. The false inner case begins to the right of the keyboard, and continues backward only far enough to provide a slot to support the jack rail.
The case also gives the harpsichord its external appearance and protects the instrument. A large harpsichord is, in a sense, a piece of furniture, as it stands alone on legs and may be styled in the manner of other furniture of its place and period. Early Italian instruments, on the other hand, were so light in construction that they were treated rather like a violin: kept for storage in a protective outer case, and played after taking it out of its case and placing it on a table.
[4] Such tables were often quite high – until the late 18th century people usually played standing up.
[4] Eventually, harpsichords came to be built with just a single case, though an intermediate stage also existed: the
false inner–outer, which for purely aesthetic reasons was built to look as if the outer case contained an inner one, in the old style.
[5] Even after harpsichords became self-encased objects, they often were supported by separate stands, and some modern harpsichords have separate legs for improved portability.
Many harpsichords have a lid that can be raised, a cover for the keyboard, and a stand for music.
Harpsichords have been decorated in a great many different ways: with plain buff paint (e.g. some Flemish instruments), with paper printed with patterns, with leather or velvet coverings, with
chinoiserie, or occasionally with highly elaborate painted artwork.
[6]
Variants[edit]
Harpsichord[edit]
In modern usage, "harpsichord" can mean any member of the family of instruments. More often, though, it specifically denotes a
grand-piano-shaped instrument with a roughly triangular case accommodating long
bass strings at the left and short
treble strings at the right. The characteristic profile of such a harpsichord is more elongated than a modern piano, with a sharper curve to the
bentside.
Virginals[edit]
The virginal is a smaller and simpler rectangular form of the harpsichord having only one string per note; the strings run parallel to the keyboard, which is on the long side of the case.
A spinet is a harpsichord with the strings set at an angle (usually about 30 degrees) to the keyboard. The strings are too close together for the jacks to fit between them. Instead, the strings are arranged in pairs, and the jacks are in the larger gaps between the pairs. The two jacks in each gap face in opposite directions, and each plucks a string adjacent to a gap.
The English diarist
Samuel Pepys mentions his "tryangle" several times. This was not the percussion instrument that we call
triangle today; rather, it was a name for octave-pitched spinets, which were triangular in shape.
Clavicytherium[edit]
Main article:
Clavicytherium
A clavicytherium is a harpsichord with the soundboard and strings mounted vertically facing the player, the same space-saving principle as an
upright piano.
[7] In a clavicytherium, the jacks move horizontally without the assistance of gravity, so that clavicytherium actions are more complex than those of other harpsichords.

An ottavino built by Arnold Dolmetsch in 1923, and modeled after a 1698 instrument by Joannes Carcassi
Clavicymbalum[edit]
Main article:
Clavicymbalum
An early relative of the harpsichord, first attested in 1323, with an unusual jack system, and lacking any method to dampen a string once sounded.
Ottavino[edit]
Ottavini are small spinets or virginals at
four foot pitch. Harpsichords at octave pitch were more common in the early Renaissance, but lessened in popularity later on. However, the ottavino remained very popular as a domestic instrument in Italy until the 19th century. In the Low Countries, an ottavino was commonly paired with an
8' virginals, encased in a small cubby under the soundboard of the larger instrument. The ottavino could be removed and placed on top of the virginal, making in effect a double manual instrument. These are sometimes called 'mother-and-child'
[8] or 'double' virginals.
[9]
The
archicembalo, built in the 16th century, had an unusual keyboard layout, designed to accommodate variant
tuning systems demanded by compositional practice and theoretical experimentation. More common were instruments with
split sharps, also designed to accommodate the tuning systems of the time.
Pedal Harpsichord: Occasionally, harpsichords were built which included another set or sets of strings underneath and operated by pedals which pluck the lowest keys of the harpsichord. Although there are no known extant pedal harpsichords from the 18th century or before, from Adlung (1758): the lower set of usually 8' strings "...is built like an ordinary harpsichord, but with an extent of two octaves only. The jacks are similar, but they will benefit from being arranged back to back, since the two [bass] octaves take as much space as four in an ordinary harpsichord
[10] Prior to 1980 when Keith Hill introduced his design for a pedal harpsichord, most pedal harpsichords were built based on the designs of extant pedal pianos from the 19th century, in which the instrument is as wide as the pedalboard. While these were mostly intended as practice instruments for organists
[citation needed], a few pieces are believed to have been written specifically for the pedal harpsichord.
[citation needed] However, the set of pedals can augment the sound from any piece performed on the instrument, as demonstrated on several albums by
E. Power Biggs.
[11]
Compass and pitch range[edit]
On the whole, earlier harpsichords have smaller
ranges than later ones, although there are many exceptions. The largest harpsichords have a range of just over five
octaves, and the smallest have under four. Usually, the shortest keyboards were given extended range in the bass with a "
short octave". The traditional pitch range for a 5-octave instrument is F1 - F6 (FF - f3).
Tuning pitch is often taken to be a=415 Hz, roughly a semitone lower than the modern standard concert pitch of a=440 Hz. An accepted exception is for French baroque repertoire, which is often performed with a=392 Hz, approximately a semitone lower again. See
Jean-Philippe Rameau's
Treatise on Harmony (1722) [Dover Publications], Book One, chapter five, for insight into French baroque tuning; "Since most of these semitones are absolutely necessary in the tuning of organs and other similar instruments, the following chromatic system has been drawn up." Tuning an instrument nowadays usually starts with setting an A; historically it would commence from a C or an F.
Some modern instruments are built with keyboards that can shift sideways, allowing the player to align the mechanism with strings at either a=415 Hz or a=440 Hz. If a tuning other than equal temperament is used, the instrument requires retuning once the keyboard is shifted.
[12]
History[edit]

An early diagram of a vertical harpsichord (clavicytherium) by
Arnault de Zwolle, ca. 1430
|
|
Performed by Robert Schröter on a French harpsichord
Performed by Martha Goldstein on a Flemish harpsichord
Performed by Sylvia Kind on a harpsichord of the type made in the early 20th century
|
| Problems playing these files? See media help. |
The harpsichord was most probably invented in the late Middle Ages. By the 16th century, harpsichord makers in Italy were making lightweight instruments with low string tension. A different approach was taken in the
Southern Netherlands starting in the late 16th century, notably by the
Ruckers family. Their harpsichords used a heavier construction and produced a more powerful and distinctive tone. They included the first harpsichords with two keyboards, used for
transposition.
The Flemish instruments served as the model for 18th century harpsichord construction in other nations. In France, the double keyboards were adapted to control different choirs of strings, making a more musically flexible instrument. Instruments from the peak of the French tradition, by makers such as the
Blanchet family and
Pascal Taskin, are among the most widely admired of all harpsichords, and are frequently used as models for the construction of modern instruments. In England, the
Kirkman and
Shudi firms produced sophisticated harpsichords of great power and sonority. German builders extended the sound repertoire of the instrument by adding
sixteen foot and
two foot choirs; these instruments have recently served as models for modern builders.
In the late 18th century the harpsichord was supplanted by the
piano and almost disappeared from view for most of the 19th century: an exception was its continued use in opera for accompanying
recitative, but the piano sometimes displaced it even there. 20th century efforts to revive the harpsichord began with instruments that used piano technology, with heavy strings and metal frames. Starting in the middle of the 20th century, ideas about harpsichord making underwent a major change, when builders such as
Frank Hubbard,
William Dowd, and
Martin Skowroneck sought to re-establish the building traditions of the Baroque period. Harpsichords of this type of historically informed building practice dominate the current scene.
Music for the harpsichord[edit]
Historical period[edit]
The great bulk of the standard repertoire for the harpsichord was written during its first historical flowering, the
Renaissance and
Baroqueeras.
The first music written specifically for solo harpsichord was published around the early 16th century. Composers who wrote solo harpsichord music were numerous during the whole Baroque era in European countries including Italy, Germany, England and France. Solo harpsichord compositions included dance
suites,
fantasias, and
fugues. Among the most famous composers who wrote for the harpsichord were the members of
English virginal school of the late Renaissance, notably
William Byrd (ca. 1540 – 1623). In France, a great number of highly characteristic solo works were created and compiled into four books of
ordres by
François Couperin (1668–1733).
Domenico Scarlatti (1685–1757) began his career in Italy but wrote most of his solo harpsichord works in Spain; his most famous work is his series of
555 harpsichord sonatas. Perhaps the most celebrated composer who wrote for the harpsichord was
J. S. Bach (1685–1750), whose solo works (for instance, the
Well-Tempered Clavier and the
Goldberg Variations), continue to be performed very widely, often on the piano. Bach was also a pioneer of the harpsichord concerto, both in
works designated as such, and in the harpsichord part of his
Fifth Brandenburg Concerto.
Two of the most prominent composers of the
Classical era,
Joseph Haydn (1732–1809) and
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (1756–1791), wrote harpsichord music. For both, the instrument featured in the earlier period of their careers and was abandoned once they had shifted their efforts to the piano.
Besides solo works, the historical harpsichord was widely used for accompaniment in the
basso continuo style (a function it maintained in
operatic recitative even into the 19th century).
Music written for the revived harpsichord[edit]
Through the 19th century, the harpsichord was almost completely supplanted by the piano. In the 20th century, composers returned to the instrument, as they sought out variation in the sounds available to them. Under the influence of
Arnold Dolmetsch, the
harpsichordists Violet Gordon-Woodhouse (1872–1951) and in France,
Wanda Landowska (1879–1959), were at the forefront of the instrument's renaissance.
Concertos for the instrument were written by
Francis Poulenc (the
Concert champêtre, 1927–28), and
Manuel de Falla.
Elliott Carter's
Double Concerto is scored for harpsichord, piano and two chamber
orchestras. For a detailed account of music composed for the revived harpsichord, see
Contempory harpsichord.




















