About Mensa National Groups https://www.mensa.org/national-groups
© 2000, 2010 Mensa International Limited. All rights reserved.
Mensa International Limited is a company registered in England and Wales under registration number 00848100.
Mensa's registered office is Slate Barn, Church Lane, Caythorpe, NG32 3EL, United Kingdom
MENSA is registered around the world as a trademark/service mark of Mensa International Limited and/or affiliated national Mensa organizations.
The Mensa logo is a registered trademark of Mensa International Limited.
Mensa does not hold any opinion, nor does it have or express any political or religious views.
Mensa, the high IQ society, provides a forum for intellectual exchange among its members. There are members in more than 100 countries around the world.
Activities include the exchange of ideas through lectures, discussions, journals, special-interest groups, and local, regional, national and international gatherings; the investigations of members' opinions and attitudes; and assistance to researchers, inside and outside Mensa, in projects dealing with intelligence or Mensa.
This is how members see Mensa https://www.mensa.org/about-us
© 2000, 2010 Mensa International Limited. All rights reserved.
Mensa International Limited is a company registered in England and Wales under registration number 00848100.
Mensa's registered office is Slate Barn, Church Lane, Caythorpe, NG32 3EL, United Kingdom
MENSA is registered around the world as a trademark/service mark of Mensa International Limited and/or affiliated national Mensa organizations.
The Mensa logo is a registered trademark of Mensa International Limited.
Mensa does not hold any opinion, nor does it have or express any political or religious views.
Mensa's registered office is Slate Barn, Church Lane, Caythorpe, NG32 3EL, United Kingdom
MENSA is registered around the world as a trademark/service mark of Mensa International Limited and/or affiliated national Mensa organizations.
The Mensa logo is a registered trademark of Mensa International Limited.
Mensa does not hold any opinion, nor does it have or express any political or religious views.
~ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intelligence_quotient#Current_tests :
Current tests[edit]
There are a variety of individually administered IQ tests in use in the English-speaking world.[33][34] The most commonly used individual IQ test series is the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale for adults and the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children for school-age test-takers. Other commonly used individual IQ tests (some of which do not label their standard scores as "IQ" scores) include the current versions of the Stanford-Binet, Woodcock-Johnson Tests of Cognitive Abilities, the Kaufman Assessment Battery for Children, the Cognitive Assessment System, and the Differential Ability Scales.
IQ tests measuring adult intelligence also includes:
- Stanford–Binet Intelligence Scales
- Woodcock–Johnson Tests of Cognitive Abilities
- Raven's Progressive Matrices
- Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale
- Cattell Culture Fair III
- Reynolds Intellectual Assessment Scales
- Thurstone's Primary Mental Abilities [35][36]
- Differential Ability Scales
- Kaufman Brief Intelligence Test[37]
- Multidimensional Aptitude Battery II
- Das–Naglieri cognitive assessment system
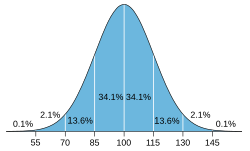
IQ scales are ordinally scaled.[38][39][40][41][42] While one standard deviation is 15 points, and two SDs are 30 points, and so on, this does not imply that mental ability is linearly related to IQ, such that IQ 50 means half the cognitive ability of IQ 100. In particular, IQ points are not percentage points.
On a related note, this fixed standard deviation means that the proportion of the population who have IQs in a particular range is theoretically fixed, and current Wechsler tests only give Full Scale IQs between 40 and 160. This should be borne in mind when considering reports of people with much higher IQs.[43][44]
Mensa International
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 | |
| Formation | 1 October 1946[1] |
|---|---|
| Legal status | Non-profit company |
| Purpose | High IQ society |
| Headquarters | Slate Barn, Church Lane,Caythorpe, Lincolnshire,England, U.K. |
| Location |
|
Membership
| over 121,000[2] |
| Website | mensa |
Mensa is the largest and oldest high IQ society in the world.[3][4][5] It is a non-profit organization open to people who score at the 98thpercentile or higher on a standardized, supervised IQ or other approved intelligence test.[6][7] Mensa formally comprises national groups and the umbrella organization Mensa International, with a registered office in Caythorpe, Lincolnshire, England[8] (which is separate from the British Mensa office in Wolverhampton[9]). The word mensa (/ˈmɛnsə/; Latin: [ˈmensa]) means "table" in Latin, as is symbolized in the organization's logo, and was chosen to demonstrate the round-table nature of the organization; the coming together of equals.[10]
Contents
[hide]Founding[edit]
Roland Berrill, an Australian barrister, and Dr. Lancelot Ware, a British scientist and lawyer, founded Mensa at Lincoln College, in Oxford, England, in 1946. They had the idea of forming a society for very intelligent people, the only qualification for membership being a high IQ.[6] It was to be non-political and free from all other social distinctions (racial, religious, etc.).[10]
American Mensa was the second major branch of Mensa. Its success has been linked to the efforts of its early and longstanding organizer, Margot Seitelman.[11]
Membership requirement[edit]
Mensa's requirement for membership is a score at or above the 98th percentile on certain standardised IQ or other approved intelligence tests, such as the Stanford–Binet Intelligence Scales. The minimum accepted score on the Stanford–Binet is 132, while for the Cattell it is 148.[12] Most IQ tests are designed to yield a mean score of 100 with astandard deviation of 15; the 98th-percentile score under these conditions is 130.
Most national groups test using well established IQ test batteries, but American Mensa has developed its own application exam. This exam is proctored by American Mensa and does not provide a score comparable to scores on other tests; it serves only to qualify a person for membership.[citation needed] In some national groups, a person may take a Mensa-offered test only once, although one may later submit an application with results from a different qualifying test.[12]
Mission[edit]
Mensa's constitution lists three purposes: "to identify and to foster human intelligence for the benefit of humanity; to encourage research into the nature, characteristics, and uses of intelligence; and to provide a stimulating intellectual and social environment for its members".[13]
To this end, the organization is also involved with programs for gifted children, literacy, and scholarships, and it also holds numerous gatherings.
Organizational structure[edit]
Mensa International consists of more than 121,000 members,[2] in 50 national groups. Individuals who live in a country with a national group join the national group, while those living in countries without a recognized chapter may join Mensa International directly. The largest national groups are[14] American Mensa, with more than 57,000 members,[15]British Mensa, with over 21,000 members,[16] and Mensa Germany, with more than 11,000 members.[17] Larger national groups are further subdivided into local groups. For example, American Mensa has 134 local groups, with the largest having over 2,000 members and the smallest having fewer than 100. Some members even live in the smallest country in the world.[18]
Members may form Special Interest Groups (SIGs) at international, national, and local levels; these SIGs represent a wide variety of interests, both commonplace and obscure, ranging from motorcycle clubs to entrepreneurial co-operations. Some SIGs are associated with various geographic groups, whereas others act independently of official hierarchy. There are also electronic SIGs (eSIGs), which operate primarily as e-mail lists, where members may or may not meet each other in person.
The Mensa Foundation, a separate charitable U.S. corporation, edits and publishes its own Mensa Research Journal, in which both Mensans and non-Mensans are published on various topics surrounding the concept and measure of intelligence. The national groups also issue periodicals, such as Mensa Bulletin, the monthly publication of American Mensa,[19] and Mensa Magazine, the monthly publication of British Mensa.[20]
Gatherings[edit]
Mensa has many events for members, from the local to the international level. Several countries hold a large event called the Annual Gathering (AG). It is held in a different city every year, with speakers, dances, leadership workshops, children's events, games, and other activities. The American and Canadian AGs are usually held during the American Independence Day (4 July) or Canada Day (1 July) weekends respectively.
There are also smaller gatherings called Regional Gatherings (RGs) held in various cities that attract members from large areas; the largest in the United States is held in the Chicago area around Halloween, and features a costume party for which many members create pun-based costumes.
In 2006, the Mensa World Gathering[21] was held from 8–13 August in Orlando, Florida to celebrate the 60th anniversary of the founding of Mensa. An estimated 2,500 attendees from over 30 countries gathered for this celebration. The International Board of Directors also had a formal meeting there. In 2010, a joint American-Canadian Annual Gathering was held in Dearborn, Michigan, to mark the 50th anniversary of Mensa in North America; this is one of several times the US and Canada AGs have been combined. Other multinational gatherings are the European Mensas Annual Gathering (EMAG), and the Asian Mensa Gathering (AMG).
Since 1990, American Mensa has also sponsored the annual Mensa Mind Games competition, whereat the Mensa Select award is given by American Mensa to five board games that are "original, challenging, and well designed".[22][23]
Individual local groups and their members also host smaller events for members and their guests. Lunch or dinner events, lectures, tours, theatre outings, and games nights are all common.
Publications[edit]
All Mensa groups publish members-only newsletters or magazines, which include articles and columns written by members, and information about upcoming Mensa events. Examples include the American Mensa Bulletin,[24] the British Mensa magazine,[25] Serbian MozaIQ,[26] the Australian TableAus,[27] the Mexican El Mensajero,[28] and the FrenchContacts.[29] Some local or regional groups have their own newsletter (for example in USA, UK, Germany, and France).
Mensa International publishes an Mensa World Journal, which "contains views and information about Mensa around the world". This journal is generally included in each national magazine.[30][31][32]
Mensa also publishes the Mensa Research Journal, which "highlights scholarly articles and recent research related to intelligence". Unlike most Mensa publications, this journal is available to non-members.[33]
Demographics[edit]
All national and local groups welcome children; many offer activities, resources, and newsletters specifically geared toward gifted children and their parents. Both American Mensa's youngest member (Christina Brown)[34] and British Mensa's youngest member (Adam Kirby) joined at the age of two.[35] The current youngest member of Mensa is Adam Kirby, from Mitcham, Surrey, UK who was invited to join at the age of two years and four months and gained full membership at the age of two years five months. He scored 141 on the Stanford-Binet IQ test.[35][36] Elise Tan-Roberts of the UK is the youngest person ever to join Mensa, having gained full membership at the age of two years and four months.[35][37]
According to American Mensa's website (as of 2013), 38 percent of its members are baby boomers between the ages of 51 and 68, 31 percent are Gen-Xers between the ages of 27 and 48, and more than 2,600 members are under the age of 18. There are more than 1,800 families in the United States with two or more Mensa members.[38] In addition, the American Mensa general membership is "66 percent male, 33 percent female". The aggregate of local and national leadership is distributed equally between the sexes.[38]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ "Mensa is 65 on 1st October – how Brilliant is that?". Mensa International. Retrieved30 August 2014.
- ^ a b Minutes of the meeting of the International Board of Directors of the international organization Mensa (PDF), Calgary, Canada: Mensa International, 20–22 September 2013, p. 2, retrieved 13 July 2014 [Requires membership]
- ^ Percival, Matt (8 September 2006). "The Quest for Genius". CNN. Retrieved30 October 2007.
- ^ Moore, Hilary. "American Mensa and Activepackets Team to Provide Mobile Users With Mensa Genius Challenge". American Mensa. Retrieved 30 October 2007.
- ^ Sharma, Mukul (30 January 2007). "IQ tests are about innate intelligence". The Times of India. India. Retrieved 3 November 2007.
- ^ a b "Mensa Information". Mensa International.
- ^ a b "FAQs - Full list". British Mensa. Retrieved 13 July 2014.
- ^ "Home." Mensa International. Retrieved 11 May 2010. "Mensa's registered office is Slate Barn, Church Lane, Caythorpe, NG32 3EL, United Kingdom."
- ^ "Contact Us". British Mensa. Retrieved 5 November 2015.
- ^ a b "About Mensa International". Mensa International. Retrieved 2013-09-17.
- ^ Victor Serebriakoff (1986). Mensa - The Society for the Highly Intelligent. Stein and Day. p. 73. ISBN 0-8128-3091-1.
- ^ a b "Submit Test Scores". American Mensa. Retrieved 2 June 2011.
- ^ "The Constitution of Mensa" (PDF). Mensa International. Retrieved 2012-10-13.
- ^ Stanislav Dimov (22 October 2011). "Thinking lessons introduced at school". Europost. Retrieved 13 July 2014.
- ^ "American Mensa". American Mensa. Retrieved 13 July 2014.
- ^ "British Mensa". British Mensa. Retrieved 13 July 2014.
- ^ "Mensa: Ein Netzwerk für Hochbegabte". Mensa Germany. Retrieved 13 July 2014.
- ^ "Mensa". Sapienza University of Rome. Retrieved 18 October 2015.
- ^ "Mensa Bulletin". American Mensa. Retrieved 11 October 2007.
- ^